Sample questions
Sample questions
Classes and inheritance
Question 1:
The below diagram illustrates the relation between the classes and their methods and fields, the architecture of the program is often presented by such a diagram.
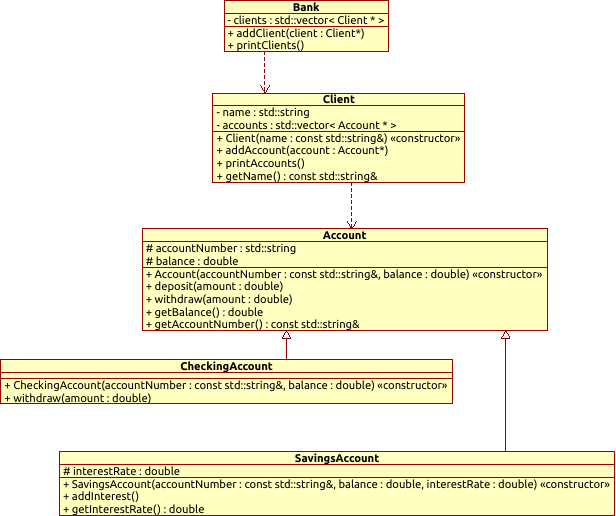
based on the given diagram write a program that presents a banking system. Create instances of the classes in main as convenient and call its public methods with appropriate parameters.
CheckingAccount should charge a 1.50 transaction fee for each withdrawal.
Template:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
int main(){
// Create accounts using std::make_unique
std::unique_ptr<Account> account1 = // TODO: complete using make_unique
std::unique_ptr<SavingsAccount> account2 = // TODO: complete using make_unique
std::unique_ptr<CheckingAccount> account3 = // TODO: complete using make_unique
// ... Deposit and withdraw operations ...
// TODO: for account1 use deposit and withdraw
// TODO: for account2 use deposit and addInterest
// TODO: for account3 use withdraw
// Create clients and add accounts using std::move
std::unique_ptr<Client> client1 = // TODO: complete using make_unique
// TODO: for client1 add account1 and account2
std::unique_ptr<Client> client2 = // TODO: complete using make_unique
// TODO: for client2 add account3
// Create bank and add clients using std::move
Bank bank;
// TODO: for bank add client1 and client2
// Print bank clients and their accounts
bank.printClients();
return 0;
}
Answer 1:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
class Account {
protected:
std::string accountNumber;
double balance;
public:
Account(const std::string& accountNumber, double balance)
: accountNumber(accountNumber), balance(balance) {}
void deposit(double amount) {
balance += amount;
std::cout << "Deposit successful. New balance: " << balance << std::endl;
}
void withdraw(double amount) {
if (balance >= amount) {
balance -= amount;
std::cout << "Withdrawal successful. New balance: " << balance << std::endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "Insufficient funds. Balance: " << balance << std::endl;
}
}
double getBalance() const {
return balance;
}
const std::string& getAccountNumber() const {
return accountNumber;
}
};
class CheckingAccount : public Account {
public:
CheckingAccount(const std::string& accountNumber, double balance)
: Account(accountNumber, balance) {}
void withdraw(double amount) {
// Charge a $1.50 transaction fee for each withdrawal
double totalAmount = amount + 1.5;
if (balance >= totalAmount) {
balance -= totalAmount;
std::cout << "Withdrawal successful. New balance: " << balance << std::endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "Insufficient funds. Balance: " << balance << std::endl;
}
}
};
class SavingsAccount : public Account {
protected:
double interestRate;
public:
SavingsAccount(const std::string& accountNumber, double balance, double interestRate)
: Account(accountNumber, balance), interestRate(interestRate) {}
void addInterest() {
double interest = balance * interestRate / 100;
balance += interest;
std::cout << "Interest added. New balance: " << balance << std::endl;
}
double getInterestRate() const {
return interestRate;
}
};
class Client {
private:
std::string name;
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Account>> accounts;
public:
Client(const std::string& name)
: name(name) {}
void addAccount(std::unique_ptr<Account> account) {
accounts.push_back(std::move(account));
}
void printAccounts() const {
std::cout << "Accounts for " << name << ":\n";
for (const auto& account : accounts) {
std::cout << account->getAccountNumber() << " - $" << account->getBalance() << "\n";
}
}
const std::string& getName() const {
return name;
}
};
class Bank {
private:
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Client>> clients;
public:
void addClient(std::unique_ptr<Client> client) {
clients.push_back(std::move(client));
}
void printClients() const {
std::cout << "Clients:\n";
for (const auto& client : clients) {
std::cout << client->getName() << "\n";
client->printAccounts();
std::cout << "\n";
}
}
};
int main() {
// Create accounts using std::make_unique
std::unique_ptr<Account> account1 = std::make_unique<Account>("A10001", 5000);
std::unique_ptr<SavingsAccount> account2 = std::make_unique<SavingsAccount>("S10001", 10000, 2.5);
std::unique_ptr<CheckingAccount> account3 = std::make_unique<CheckingAccount>("C10001", 2000);
// ... Deposit and withdraw operations ...
account1->deposit(1000);
account1->withdraw(2000);
account2->deposit(500);
account2->addInterest();
account3->withdraw(500);
// Create clients and add accounts using std::move
std::unique_ptr<Client> client1 = std::make_unique<Client>("John Doe");
client1->addAccount(std::move(account1));
client1->addAccount(std::move(account2));
std::unique_ptr<Client> client2 = std::make_unique<Client>("Jane Smith");
client2->addAccount(std::move(account3));
// Create bank and add clients using std::move
Bank bank;
bank.addClient(std::move(client1));
bank.addClient(std::move(client2));
// Print bank clients and their accounts
bank.printClients();
return 0;
}Question 2:
Create methods for Stack class that allows for the calls in the main function. It is supposed to keep stacked intigers.
Template:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Stack {
public:
Stack(std::vector<int> numbers)
{
\\ TODO
}
\\ TODO
private:
std::vector<int> _numbers;
};
int main()
{
Stack stack1({3, 4, 3, 5, 4, 9});
Stack stack2({3, 4, 7, 11});
std::cout << "Stack 1: " << stack1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "Stack 2: " << stack2 << std::endl;
Stack concatenate = stack1 + stack2; //merge the stacks together: {3, 3, 4} + {1, 2, 3} gives {3, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3}
std::cout << concatenate << std::endl;
stack1--; //remove the top element from stack: {3, 3, 4}-- gives {3, 3}
std::cout << "Top removed: " << stack1 << std::endl;
stack1 << 15 << 8; // add new element on top of the stack
std::cout << "New added: " << stack1 << std::endl;
return 0;
}Authors: Kamil Młodzikowski, Iman Esfandiyar